Confused about idioms vs colloquialisms and the part they play in our daily conversations?
Simply put, an idiom is a fixed phrase with a figurative meaning, whereas a colloquialism is an informal word or phrase specific to everyday language and often to a particular region.
They are both common linguistic devices that native English speakers use in everyday conversation – often without really thinking about it. But as an English learner, you need to be able to recognize and understand these expressions.
In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at the difference between idioms and colloquialisms, and how to use them correctly.

What is the difference between an idiom and a colloquialism?
An idiom is a phrase with a non-literal meaning. For example, ‘let the cat out of the bag’ means ‘reveal a secret’, but you couldn’t guess that from seeing the phrase alone.
Colloquialisms are informal words or phrases that occur in everyday dialogue, often specific to a particular region. For instance, people from different parts of a country might have different ways of greeting one another informally.
Some colloquialisms take the form of idioms, but most colloquial language is not idiomatic.
Examples of common idioms
Here are some examples of idioms used in English that perfectly demonstrate their non-literal meanings.
| Idiom | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Have cold feet | Change your mind about doing something because of nervousness or fear |
| Add fuel to the fire | Make an already bad situation worse |
| Hit the nail on the head | Do something exactly right |
| Neither here nor there | Not relevant or important |
| Get down to business | Begin a task or focus on work |
| On the house | Provided free of charge |
| Tighten your belt | Reduce spending and live more frugally |
Examples of English colloquialisms
Here are some examples of colloquial expressions that are used in everyday speech in informal settings:
| Standard expression | Colloquial expressions |
|---|---|
Hello | Hey Alright? What’s up? Yo Hiya |
Goodbye | Bye Seeya Catch you later Taraa (British) Later(s) |
Thank you | Cheers (British) Thanks heaps Thanks a lot Ta (British) You’re a lifesaver |
You’re welcome | It’s nothing All good No worries No problem Sure thing Anytime |
How are you? | How’s it going? What’s new? What’s up? How’s life? |
It’s interesting to look at regional colloquialisms, too.
In the UK, for instance, something as simple as a small round bread has multiple different names depending on where you are in the country. This map published by Cambridge University illustrates the differences:
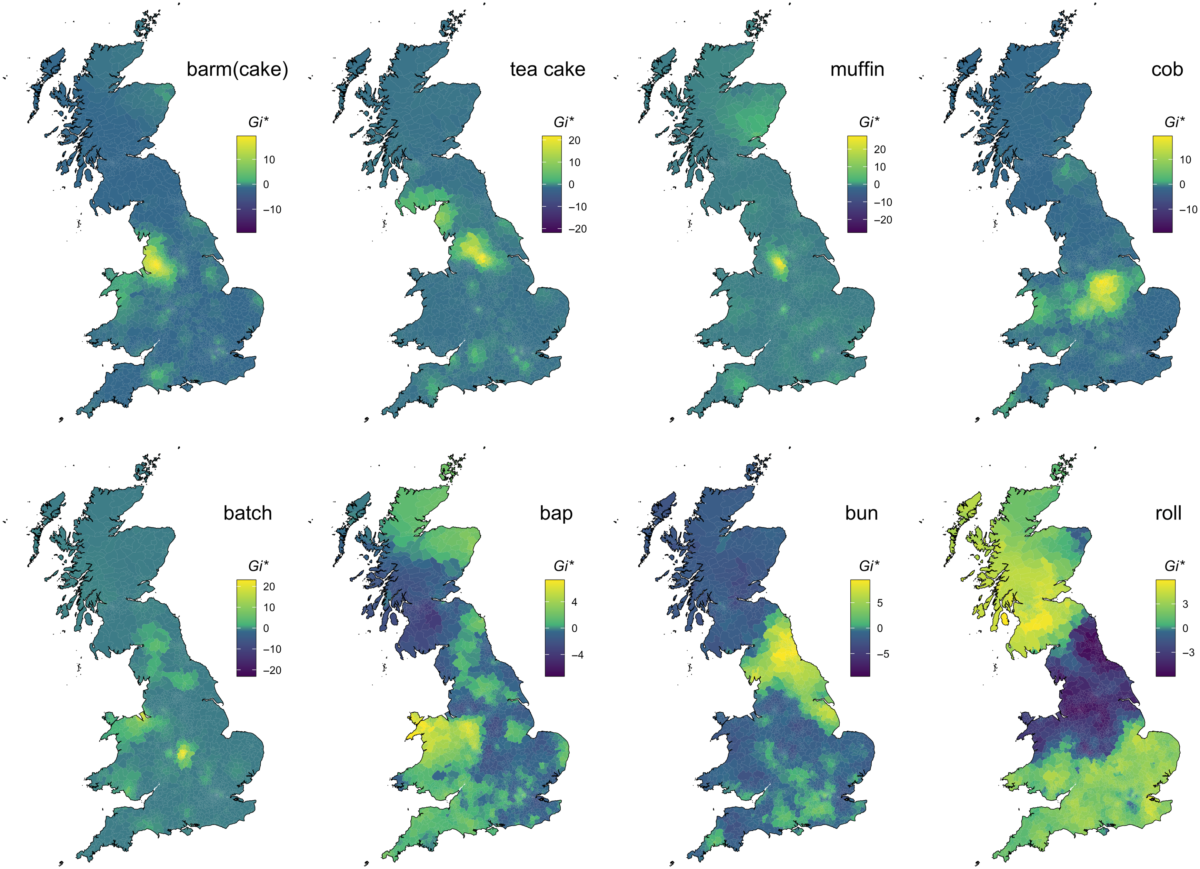
Statistician Josh Katz’s book Speaking American highlights some fascinating differences in American English.
One example is ‘trash can’, preferred in the south, vs ‘garbage can’, preferred in the north. In the UK, this could be called a ‘litter bin’, a ‘rubbish bin’, or just a ‘bin’.

You can discover more British vs American word differences in our separate article.
Colloquialisms vs slang and jargon
Slang and jargon are similar to colloquialisms in that they are all types of informal language used by certain people.
The main difference between colloquialisms and slang is that slang appears in specific social groups or classes (e.g. teenagers, doctors) whereas colloquialisms are used by ordinary people of all ages and backgrounds.
Jargon is similar to slang, except that it is specific to a certain occupation, industry, or activity (e.g. medicine, architecture, marketing).
When to use colloquialisms and idioms
As a general rule, we do not use colloquial terms, slang, or idioms in formal situations. They may be considered unprofessional and can even lead to misunderstandings.
In professional settings, idioms are generally accepted and some casual language may be appropriate, depending on the formality of the context.
When speaking or writing to friends in casual settings, colloquial usage of language is appropriate provided the other person is also familiar with it.
Colloquialisms are sometimes used in literature to emphasize the accent or background of a character.

How to master colloquialisms and idioms when learning English
Becoming fluent in English requires familiarity with the expressions regularly used by native speakers, including idioms and colloquialisms. They will help you converse more naturally and better comprehend the different people you meet.
Idioms, by their very nature, cannot be understood from their words alone. As you explore the English language, you must learn the meaning of each idiomatic expression you discover. On the plus side, idioms are widely used among native speakers – although there are some American idioms and British idioms to be aware of.
When it comes to learning colloquialisms, focus on those commonly used in the area you’ll be living in or visiting. For example, if you’re going to study English in London, there’s not much point learning colloquialisms used exclusively in the southern US states.
To overcome the challenges of figurative meanings and regional variations, you can try:
- Practicing with native speakers and asking them to explain any colloquial terms they use
- Studying phrases in context
- Using language apps and online resources to expand your vocabulary
- Listening to podcasts or watching TV shows and movies featuring a variety of accents and dialects
When faced with unfamiliar terms, you may be able to use the context to guess their meaning. If not, an online dictionary like thefreedictionary.com should have a definition.
Idioms vs colloquialisms: Summary
Now we’ve covered the main differences between colloquialisms and idioms, you should be more comfortable identifying them and using them yourself when appropriate.
Remember that the words people use change across regions and social groups. A term that’s considered extremely informal in one place might be acceptable in more formal settings elsewhere.
As you expose yourself to different forms of English through media, traveling, and meeting new people, you can discover new expressions and improve your communication skills.
Next, why not look at idioms vs euphemisms – another common linguistic device.
FAQs
What is the key difference between an idiom and a colloquialism?
The key difference between an idiom and a colloquialism lies in their meanings and usage. Idioms have figurative meanings that can’t be deduced from individual words, while colloquialisms are informal expressions specific to particular geographical areas.
Can idioms and colloquialisms be used in formal writing?
Idioms and colloquialisms should generally be avoided in formal writing to maintain professionalism and clarity in communication.
Why are idioms and colloquialisms important in language learning?
Idioms and colloquialisms are important in language learning because they are used every day by native speakers and are a sign of advanced fluency.
Is colloquialism a synonym for dialect?
Colloquialisms are part of a dialect, but the two are not synonymous. A dialect is a regional or social variety of a language, defined by the pronunciation, grammar, and words used. Colloquialisms are individual words or phrases specific to a region.



